Introduction
Budgeting for beginners can feel intimidating, especially if you’ve never tracked your spending. But it doesn’t have to be complicated. Budgeting is simply about knowing where your money goes, prioritizing essentials, and creating a plan that aligns with your goals. In this guide, we’ll break down practical steps, real-life examples, and common mistakes to avoid. Whether you’re managing personal finances, student income, or family expenses, this article will help you save more, reduce stress, and gain control over your money. By the end, you’ll be confident about making smart financial decisions and building a secure future.
Why Budgeting Matters
Understand your money flow: Track every dollar to prevent overspending.
Financial security: Build an emergency fund and prepare for unexpected expenses.
Achieve your goals: Saving for a car, vacation, or home becomes easier.
Mini-Case Study:
Sarah, a college student, tracked her $2,200 monthly income and discovered she spent $400 on coffee and eating out. Reducing this allowed her to save $200 every month.
Step 1 – Track Your Income and Expenses
Income: Include salary, freelance gigs, side hustles, and passive income.
Expenses: Separate fixed (rent, bills) from variable (groceries, entertainment).
Tools: Use apps like Mint, YNAB, or a simple spreadsheet.
Common Mistakes:
Ignoring irregular expenses such as annual subscriptions.
Overlooking small daily purchases—they add up quickly.
Step 2 – Set Realistic Budget Categories
50/30/20 Rule: 50% necessities, 30% wants, 20% savings/debt repayment.
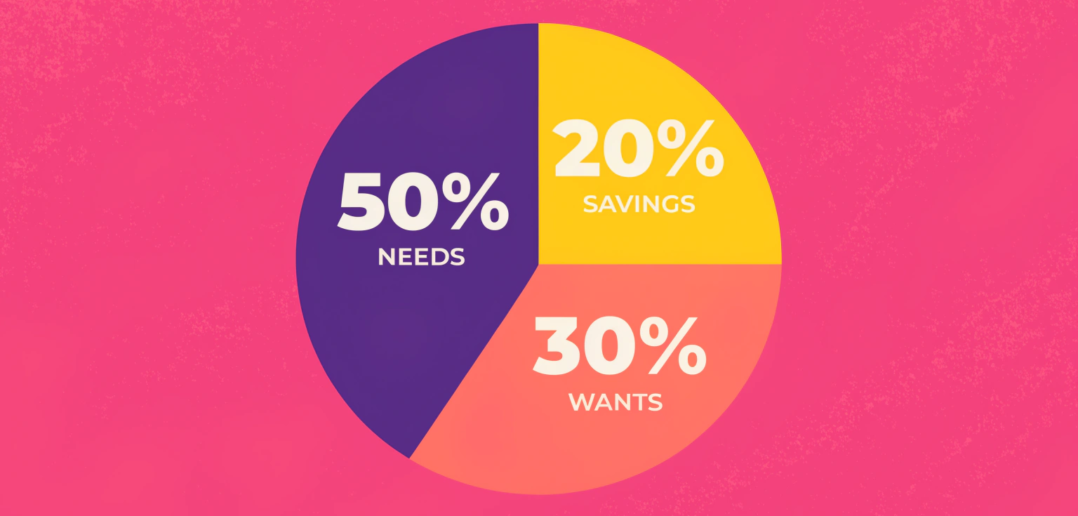
Flexible categories: Include entertainment, hobbies, and health expenses.
Prioritize goals: Emergency fund, debt payoff, or retirement savings.
Example:
Monthly Income: $3,000
$1,500 – Rent & Utilities
$900 – Wants
$600 – Savings
Mini-Case Study:
John wanted to save for a car. By allocating 20% of his $3,500 income to savings, he reached his goal in six months.
Step 3 – Create a Budget Plan
Use spreadsheets, apps, or notebooks to organize categories.
Track spending weekly and adjust categories after 1–2 months for accuracy.
Ensure savings are included as a “non-negotiable” category.
Common Mistakes:
Setting unrealistic budgets that are impossible to follow.
Forgetting to review and adjust regularly.
Step 4 – Reduce Unnecessary Expenses
Cancel unused subscriptions.
Cook at home instead of frequent takeout.
Use public transport or carpool to save on fuel.
Example:
Emily reduced her takeout spending from $300 to $150 per month, increasing her savings rate by 5%.
Step 5 – Automate Savings
Set up automatic transfers to a savings account.
Use apps that round up purchases to save extra cash.
Mini-Case Study:
Mark’s app rounded up every purchase to the nearest dollar, adding an extra $50 monthly to his savings without him noticing.
Common Budgeting Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring irregular or unexpected expenses
Forgetting small daily purchases
Being too rigid—allow flexibility
Not adjusting the budget when income changes
Forgetting long-term financial goals
FAQs (SEO-Optimized)
Q1: How do I start budgeting if I have no experience?
A: Start by tracking your income and expenses for a month. Use a spreadsheet or budgeting app to categorize spending and set realistic saving goals.
Q2: What is the best budgeting method for beginners?
A: The 50/30/20 rule works well: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings or debt repayment.
Q3: How much should I save each month?
A: Aim for at least 20% of your income, but adjust based on your financial goals and obligations.
Q4: Can I budget with irregular income?
A: Yes, track your average income over 3–6 months and create a flexible plan prioritizing essentials and savings.
Q5: Which apps are best for beginners?
A: Mint, YNAB, and PocketGuard help track income, expenses, and savings.
Q6: What if I overspend one month?
A: Review your budget, adjust categories, and remember it’s about long-term consistency, not perfection.
Internal Links
Zero-Based Budgeting Method
How Much Emergency Fund Should I Save
Best Budget Planner Apps 2025
External Links
Investopedia – Budgeting Basics
NerdWallet – Best Budget Apps